In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, where software applications drive critical business operations, manual QA testing services have emerged as an indispensable foundation for ensuring software quality and reliability. Despite the 39% reduction in manual work due to AI advancements, manual testing remains critical for delivering exceptional user experiences and maintaining software integrity.
Get a proposal today → or Speak to a QA Specialist →
Market Overview & Impact
Global Market Statistics:
- Global market value: $4.5 billion in 2024, projected to reach $8.2 billion by 2033
- Cost of poor quality: U.S. businesses lose approximately $3.1 trillion annually due to software defects
- Strategic importance: Manual testing serves as the first line of defense against software defects
The cost of poor software quality continues to escalate, underscoring the critical importance of implementing robust quality assurance manual testing strategies that can detect and prevent costly failures before they impact end users.
What Are Manual QA Testing Services?
Manual software testing services represent a comprehensive approach to software quality assurance where human testers systematically execute test cases, explore application functionalities, and validate software behavior against specified requirements. Unlike automated testing that relies on scripts and tools, quality assurance manual testing leverages human cognition, intuition, and domain expertise to uncover defects that might otherwise remain hidden.
Core Components of Manual QA Testing
The foundation of effective manual QA services rests on several critical components:
Human Cognitive Advantages:
- Contextual understanding - Ability to understand user context and real-world scenarios
- Usability assessment - Identification of interface issues and user experience problems
- Adaptive testing - Real-time strategy adjustment based on observations
- Edge case discovery - Finding unexpected behaviors and boundary conditions
Exploratory Capabilities:
- Subjective evaluation - Assessing UI aesthetics and workflow intuitiveness
- User perspective - Understanding how real users will interact with applications
- Pain point identification - Discovering usability barriers that impact adoption
- Dynamic investigation - Following unexpected paths to reveal critical defects
Manual vs Automated Testing: When to Choose Manual
The decision between manual testing vs automation requires careful consideration of multiple factors:
Manual Testing is Superior For:
- Small projects with limited budgets
- Frequent UI changes that require constant test updates
- Exploratory testing requiring human intuition
- Usability evaluation needing subjective assessment
- Complex business workflows requiring contextual understanding
ROI Considerations:
- Manual testing delivers better ROI for smaller, short-term projects
- Automation provides superior ROI for large, repetitive testing requirements
- Manual testing essential when human judgment is required
Types of Manual QA Testing Services
The landscape of manual testing services types encompasses diverse testing approaches designed to address specific quality assurance testing requirements.
Functional Testing Services
Functional manual testing forms the cornerstone of quality assurance, focusing on verifying that software applications perform their intended functions correctly.
Key Focus Areas:
- Business logic validation - Ensuring correct processing of business rules
- Data processing verification - Validating input/output handling
- User workflow testing - Confirming end-to-end process functionality
- System integration testing - Verifying component interactions
- API functionality - Testing service interfaces and data exchange
- Database operations - Validating data storage and retrieval
Testing Approaches:
- Systematic verification through carefully designed test scenarios
- Real-world usage pattern simulation
- Boundary condition and error handling validation
- Input processing and output generation testing
Usability and UX Testing
Manual usability testing represents a critical component of user-centered design validation.
Core Evaluation Areas:
- Interface intuitiveness - Assessing ease of navigation and use
- Visual appeal - Evaluating design aesthetics and consistency
- Workflow efficiency - Identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- Accessibility compliance - Ensuring inclusive design implementation
- User satisfaction - Measuring overall user experience quality
Testing Methodology:
- Human judgment assessment of subjective interface elements
- User interaction analysis and pain point identification
- Navigation flow validation and optimization recommendations
- Design consistency evaluation across platforms
Exploratory Testing Services
Exploratory manual testing leverages human creativity and domain expertise to discover defects through unscripted, investigative approaches.
Key Characteristics:
- Simultaneous learning - Test design and execution happen concurrently
- Adaptive strategies - Real-time adjustment based on findings
- Creative investigation - Using intuition to explore application boundaries
- Unscripted approach - No predetermined test cases or scripts
Value Proposition:
- Discovery of edge cases and unexpected behaviors
- Integration issue identification
- Unusual input combination testing
- Potential failure scenario investigation
Accessibility Testing (WCAG Compliance)
Manual accessibility testing ensures applications comply with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.2, which introduced nine new success criteria in October 2023.
WCAG 2.2 Compliance Requirements:
- Focus visibility - Clear indication of keyboard focus
- Keyboard navigation - Full functionality without mouse
- Color contrast - Sufficient contrast ratios for readability
- Assistive technology - Compatibility with screen readers and other tools
Testing Approach:
- Manual evaluation of accessibility features
- Verification of inclusive design principles
- Testing with assistive technologies
- Validation of equivalent user experiences
Cross-Browser and Device Testing
Cross-browser manual testing validates application functionality, appearance, and performance across diverse environments.
Testing Scope:
- Browser compatibility - Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge variations
- Operating systems - Windows, macOS, Linux, mobile platforms
- Device configurations - Desktops, tablets, smartphones
- Screen resolutions - Various display sizes and orientations
Validation Points:
- Rendering consistency across platforms
- Functional behavior uniformity
- Performance characteristic evaluation
- User experience consistency
Industry-Specific Manual QA Testing Services
Industry-specific manual testing addresses unique compliance testing requirements and regulatory standards.
Healthcare Manual Testing (HIPAA Compliance)
Healthcare manual testing HIPAA compliance represents a critical aspect of medical software quality assurance.
HIPAA Compliance Requirements:
- Data encryption - Protection of patient health information in transit and at rest
- Access controls - User authentication and authorization systems
- Audit logging - Comprehensive tracking of system access and changes
- Data transmission security - Secure communication protocols
Testing Focus Areas:
- Security control validation
- Patient data protection verification
- Regulatory compliance confirmation
- Privacy safeguard implementation
Financial Services QA Testing (SOX, PCI-DSS)
Financial manual testing compliance encompasses comprehensive validation against regulatory standards.
Compliance Standards:
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley) - Financial reporting accuracy and transparency
- PCI-DSS - Payment card data protection standards
- Banking regulations - Industry-specific compliance requirements
Testing Priorities:
- Transaction accuracy validation
- Security control verification
- Audit trail confirmation
- Regulatory reporting accuracy
- Fraud detection system testing
E-commerce Platform Testing
E-commerce manual testing addresses the unique challenges of online retail platforms.
Key Testing Areas:
- Payment processing - Gateway integrations and transaction handling
- Inventory management - Stock tracking and availability updates
- Shopping cart functionality - Add/remove/modify item operations
- Order fulfillment - Complete purchase process validation
- Customer accounts - Registration, login, profile management
Quality Assurance Focus:
- Product catalog accuracy
- Pricing and promotional campaign validation
- Customer communication system testing
- Security and performance verification
SaaS Application Manual Testing
SaaS manual testing services focus on validating cloud-based applications with multi-tenant architectures.
Unique SaaS Challenges:
- Multi-tenancy - Data isolation between different customers
- Scalability - Performance under varying load conditions
- Subscription management - Billing and account administration
- API integrations - Third-party service connections
Testing Approach:
- User onboarding process validation
- Data security and tenant isolation verification
- Performance consistency across user configurations
- Integration capability testing
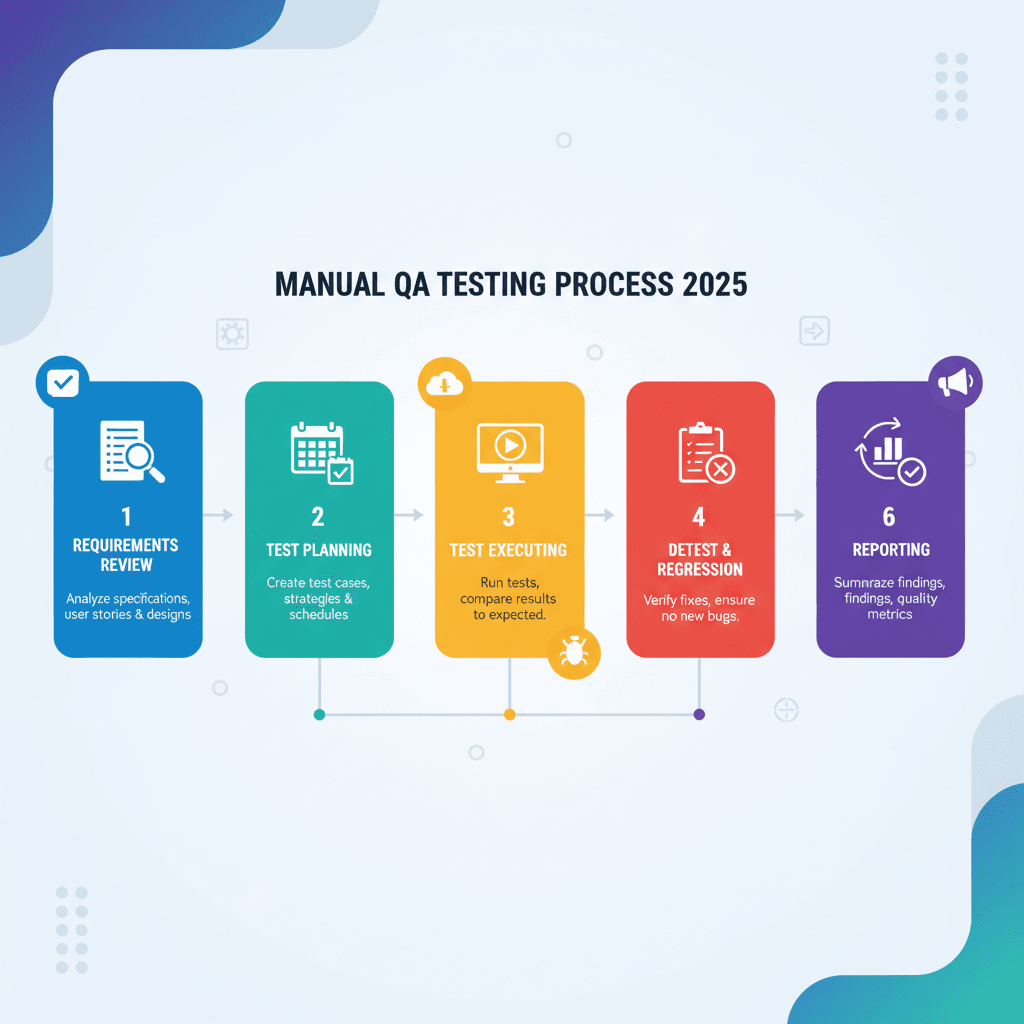
Manual QA Testing Process & Methodology
The manual testing process follows a structured QA testing methodology that ensures comprehensive coverage and reliable results.
Phase 1: Requirements Analysis and Test Planning
Test planning manual testing begins with thorough analysis of requirements, specifications, and acceptance criteria.
Planning Components:
- Stakeholder collaboration - Involving all relevant parties in planning
- Risk assessment - Identifying potential quality risks and mitigation strategies
- Resource allocation - Determining team size and skill requirements
- Timeline development - Establishing realistic testing schedules
Strategic Considerations:
- Testing scope definition and boundary establishment
- Quality objectives alignment with business goals
- Resource requirement assessment and availability confirmation
- Success criteria establishment and measurement planning
Phase 2: Test Case Design and Documentation
Manual test case design involves systematic creation of test scenarios that validate functional and non-functional requirements.
Design Principles:
- Comprehensive coverage - Addressing all requirements and user scenarios
- Structured procedures - Clear, step-by-step instructions
- Repeatable processes - Consistent execution across different testers
- Traceability - Clear links between requirements and test cases
Documentation Standards:
- Clear, actionable instructions for consistent execution
- Sufficient detail for result analysis and defect reporting
- Living documentation that evolves with requirements
- Version control and change management
Phase 3: Test Execution and Defect Management
Manual test execution involves systematic implementation of test cases with careful observation and documentation.
Execution Best Practices:
- Systematic approach - Following predefined test procedures
- Detailed observation - Careful monitoring of application behavior
- Thorough documentation - Recording results and anomalies
- Clear communication - Effective reporting to development teams
Defect Management Process:
- Comprehensive documentation - Detailed issue descriptions with reproduction steps
- Environment details - System configuration and setup information
- Impact assessment - Severity and priority determination
- Collaborative resolution - Working with development teams for efficient fixes
Phase 4: Reporting and Quality Metrics
Manual testing metrics provide quantitative insights into testing effectiveness and quality improvements.
Key Metrics:
- Test coverage analysis - Percentage of requirements validated
- Defect density measurements - Bugs per unit of code or functionality
- Trend analysis - Quality improvements over time
- Testing efficiency - Resource utilization and productivity measures
Reporting Components:
- Comprehensive test coverage reports
- Defect trend analysis and root cause identification
- Quality status dashboards and risk assessments
- Improvement recommendations and action plans
AI-Assisted Manual Testing: The Future of QA
AI-assisted manual testing represents the convergence of human expertise and artificial intelligence capabilities.
Hybrid Testing Models: Manual + AI
Hybrid manual AI testing approaches combine human cognitive abilities with AI computational power.
AI Augmentation Benefits:
- Faster test case generation - Automated creation of test scenarios
- Intelligent defect detection - Pattern recognition and anomaly identification
- Predictive analysis - Forecasting potential quality issues
- Enhanced coverage - Identifying testing gaps and optimization opportunities
Human Value Preservation:
- Creative problem-solving - Complex analysis requiring human insight
- Usability evaluation - Subjective assessment of user experience
- Exploratory testing - Adaptive investigation and discovery
- Strategic decision-making - Quality risk assessment and prioritization
AI Tools for Manual Testers
AI tools manual testing encompasses intelligent solutions that support human testers.
Available AI Capabilities:
- Visual testing - Automated UI comparison and validation
- Natural language test generation - Converting requirements to test cases
- Intelligent test data management - Automated test data creation and maintenance
- Predictive defect analysis - Identifying high-risk areas for focused testing
Implementation Approach:
- Tool selection based on specific testing needs
- Integration with existing testing workflows
- Training and adoption planning for testing teams
- Continuous evaluation and optimization of AI tool effectiveness
Manual QA Testing Pricing Models & ROI
Understanding manual testing pricing and manual QA testing cost structures is essential for optimizing quality assurance investments.
Pricing Models: Hourly vs Project vs Dedicated Team
Manual testing pricing models vary significantly based on engagement type and requirements.
Hourly Rate Structure:
- Functional testers: $10-$15 per hour
- Specialized roles: $22+ per hour (security testing, performance testing)
- Geographic variations: Rates differ by location and market conditions
- Experience levels: Senior testers command premium rates
Engagement Models:
Fixed-Price Projects:
- Benefits: Budget predictability and scope clarity
- Best for: Well-defined projects with stable requirements
- Considerations: Change management and scope creep risks
Time-and-Material:
- Benefits: Flexibility for evolving requirements
- Best for: Projects with uncertain or changing scope
- Considerations: Budget control and resource management
Dedicated Team:
- Benefits: Long-term collaboration and domain expertise
- Best for: Ongoing projects requiring specialized knowledge
- Considerations: Higher initial investment but better long-term value
ROI Calculator: Manual vs Automated Testing
Manual testing ROI calculation requires comprehensive analysis of costs and benefits.
ROI Factors:
- Direct costs - Testing team salaries, tools, and infrastructure
- Opportunity costs - Time to market and competitive advantages
- Quality benefits - Defect prevention and customer satisfaction
- Maintenance costs - Ongoing support and test case updates
Decision Framework:
- Project duration - Short-term projects favor manual testing
- Test case reusability - Repetitive tests benefit from automation
- Maintenance requirements - Consider long-term support costs
- Defect detection effectiveness - Evaluate quality outcomes
Cost Optimization Strategies
Manual testing cost optimization involves strategic approaches to maximize value.
Optimization Techniques:
- Risk-based testing - Prioritizing high-impact areas
- Early defect detection - Shifting testing left in development cycle
- Hybrid approaches - Combining manual and automated capabilities
- Resource efficiency - Optimal team size and skill mix
Budget Management:
- Focus on high-impact testing activities
- Leverage automation for repetitive tasks
- Implement AI assistance for enhanced efficiency
- Regular cost-benefit analysis and adjustment
Choosing the Right Manual QA Testing Company
Selecting an appropriate manual testing company requires careful evaluation of capabilities and cultural fit.
Key Selection Criteria
Choose manual testing company decisions should prioritize several critical factors:
Technical Capabilities:
- Industry experience - Relevant domain knowledge and expertise
- Methodology proficiency - Proven testing processes and frameworks
- Tool expertise - Familiarity with testing tools and technologies
- Quality certifications - Professional credentials and standards compliance
Operational Excellence:
- Communication skills - Clear, timely reporting and collaboration
- Scalability - Ability to adjust team size based on project needs
- Cultural alignment - Compatibility with organizational values and practices
- Quality standards - Commitment to excellence and continuous improvement
Questions to Ask Potential Vendors
Manual testing vendor evaluation should include comprehensive capability assessment:
Process and Methodology Questions:
- What testing methodologies do you follow?
- How do you ensure consistent quality across projects?
- What are your defect tracking and reporting processes?
- How do you handle changing requirements and scope adjustments?
Experience and Expertise Questions:
- What industry-specific experience do you have?
- Can you provide case studies and client references?
- What certifications do your team members hold?
- How do you stay current with testing trends and technologies?
Collaboration and Communication Questions:
- What are your communication protocols and reporting schedules?
- How do you handle escalations and issue resolution?
- What tools do you use for project management and collaboration?
- How do you ensure knowledge transfer and documentation?
Manual Testing Best Practices & Quality Standards
Manual testing best practices and QA quality standards provide frameworks for consistent, effective testing processes.
ISO 29119 Testing Standards
ISO manual testing standards provide internationally recognized frameworks for testing processes and quality management.
ISO 29119 Components:
- Test processes - Systematic approaches to test planning and execution
- Documentation standards - Consistent format for test artifacts
- Quality management - Continuous improvement and metrics tracking
- Traceability requirements - Clear links between requirements and tests
Implementation Benefits:
- Systematic testing process establishment
- Quality consistency across projects and teams
- International best practice compliance demonstration
- Improved stakeholder confidence and trust
Quality Metrics and KPIs
Manual testing KPIs enable data-driven quality management through systematic measurement.
Essential Metrics:
Coverage Metrics:
- Test coverage percentage - Requirements and code coverage ratios
- Functional coverage - Business process validation completeness
- Risk coverage - High-risk area testing thoroughness
Defect Metrics:
- Defect density - Bugs per unit of functionality or code
- Defect escape rate - Issues found in production vs. testing
- Defect resolution time - Average time from discovery to fix
Efficiency Metrics:
- Testing productivity - Test cases executed per hour/day
- Resource utilization - Tester efficiency and capacity planning
- Cost per defect - Investment required to find and fix issues
Continuous Improvement:
- Trend analysis - Identifying patterns and improvement opportunities
- Benchmark comparison - Industry standard performance evaluation
- Process optimization - Regular review and enhancement of testing practices
- Action planning - Systematic approach to implementing improvements
Manual Testing Tools & Technologies
Manual testing tools and QA testing software provide essential support throughout the testing lifecycle.
Test Management Tools
Manual testing management tools facilitate comprehensive test planning, execution, and reporting.
Leading Solutions:
TestRail:
- Comprehensive test case management and organization
- Execution tracking and progress monitoring
- Detailed reporting and analytics capabilities
- Integration with development and bug tracking tools
Jira:
- Issue tracking and project management integration
- Customizable workflows and process automation
- Comprehensive reporting and dashboard capabilities
- Extensive third-party integrations and plugins
TestLink:
- Open-source test management solution
- Requirements management and traceability
- Test execution tracking and result documentation
- Basic reporting and metrics capabilities
Key Capabilities:
- Collaborative environments - Supporting distributed testing teams
- Traceability management - Linking requirements to test cases and results
- Execution tracking - Progress monitoring and bottleneck identification
- Integration capabilities - Connecting with development tools and CI/CD pipelines
Bug Tracking and Reporting Tools
Bug tracking manual testing systems provide structured approaches to defect management.
Popular Solutions:
Bugzilla:
- Comprehensive defect lifecycle management
- Advanced search and filtering capabilities
- Customizable workflows and field configurations
- Email notifications and collaboration features
Jira:
- Integrated issue tracking and project management
- Advanced reporting and analytics capabilities
- Customizable dashboards and workflow automation
- Extensive integration ecosystem
MantisBT:
- Open-source bug tracking solution
- Simple, user-friendly interface
- Basic workflow management and reporting
- Plugin architecture for extensibility
Essential Features:
- Defect lifecycle management - From discovery to resolution
- Collaboration tools - Communication between testing and development teams
- Trend analysis - Quality improvement insights and metrics
- Integration capabilities - Connecting with development environments and tools
Future of Manual QA Testing Services
The future manual testing landscape will be shaped by manual testing trends 2025 emphasizing integration and specialization.
Emerging Technologies Impact
Manual testing emerging tech trends include specialized approaches for new technology domains.
Technology Areas:
- IoT Applications - Internet of Things device and ecosystem testing
- Blockchain Systems - Distributed ledger and smart contract validation
- AR/VR Platforms - Augmented and virtual reality experience testing
- AI Systems - Machine learning model behavior and bias testing
Testing Challenges:
- Complex interactions - Multi-device and cross-platform scenarios
- User experience validation - Immersive and novel interface testing
- Performance requirements - Real-time responsiveness and reliability
- Security considerations - Privacy and data protection in new contexts
Human Expertise Requirements:
- Adaptability - Learning new testing approaches for emerging technologies
- Creative thinking - Developing novel testing strategies
- Domain knowledge - Understanding technology-specific challenges
- User perspective - Evaluating experiences that automated tools cannot assess
Career Evolution for Manual Testers
Manual testing career future opportunities will emphasize quality engineering and strategic value creation.
Evolving Roles:
Quality Engineer:
- Strategic focus - Quality planning and risk assessment
- Process improvement - Testing methodology optimization
- Tool evaluation - Selection and implementation of testing technologies
- Stakeholder collaboration - Working with development and business teams
AI Collaboration Specialist:
- AI tool proficiency - Leveraging artificial intelligence for testing enhancement
- Human-AI workflow design - Optimizing collaboration between humans and machines
- Training and adoption - Helping teams integrate AI testing capabilities
- Quality validation - Ensuring AI-generated tests meet quality standards
User Experience Specialist:
- Usability expertise - Deep understanding of user-centered design principles
- Accessibility knowledge - Ensuring inclusive design implementation
- User research skills - Conducting testing that reflects real user needs
- Design collaboration - Working closely with UX/UI teams
Professional Development Areas:
- AI tool proficiency - Understanding and leveraging artificial intelligence
- Domain specialization - Deep expertise in specific industries or technologies
- Quality engineering principles - Strategic approach to quality management
- Leadership skills - Managing testing teams and quality initiatives
Career Advancement Strategies:
- Continuous learning - Staying current with testing trends and technologies
- Certification pursuit - Professional credentials and skill validation
- Community engagement - Participating in testing communities and conferences
- Cross-functional collaboration - Building relationships across development teams
Frequently Asked Questions
Manual testing FAQ addresses common QA testing questions that organizations face.
Q: What is the difference between manual and automated testing?
Manual testing involves human testers executing test cases and evaluating software behavior, while automated testing uses scripts and tools to perform repetitive tests.
Key Differences:
- Manual testing excels at: Exploratory testing, usability evaluation, complex scenario validation, and situations requiring human judgment
- Automated testing is ideal for: Repetitive regression testing, load testing, and scenarios with predictable outcomes
Q: When should I choose manual testing over automation?
Manual testing is preferred in several scenarios:
Optimal Use Cases:
- Exploratory testing - Discovering unknown issues and edge cases
- Usability evaluation - Assessing user experience and interface design
- Ad-hoc testing - Investigating specific issues or scenarios
- Human judgment requirements - Subjective assessment needs
- Small projects - Where automation setup costs exceed benefits
- Frequent UI changes - When interfaces change too often for stable automation
Q: How much does manual testing typically cost?
Manual testing costs vary based on multiple factors:
Hourly Rate Ranges:
- Functional testers: $10-$15 per hour
- Specialized testers: $22+ per hour (security, performance, accessibility)
- Geographic variations affect pricing significantly
- Experience levels command different rates
Project Budget Guidelines:
- Manual testing typically represents 15-25% of overall development budget
- Cost factors include: Project complexity, resource requirements, timeline constraints
- ROI considerations: Balance cost against quality improvement and risk reduction
Q: What qualifications should manual testers have?
Effective manual testers should possess a combination of technical and soft skills:
Technical Qualifications:
- ISTQB certification or similar professional credentials
- Testing tool experience - Familiarity with test management and bug tracking tools
- Methodology knowledge - Understanding of testing frameworks and best practices
- Domain expertise - Industry-specific knowledge when relevant
Essential Soft Skills:
- Analytical thinking - Ability to break down complex problems
- Attention to detail - Spotting subtle issues and inconsistencies
- Communication skills - Clear reporting and collaboration abilities
- Curiosity and persistence - Drive to explore and investigate thoroughly
Q: How can organizations measure manual testing effectiveness?
Organizations should track multiple metrics to evaluate testing effectiveness:
Key Performance Indicators:
Coverage Metrics:
- Test coverage percentage - Proportion of requirements validated
- Functional coverage - Business process testing completeness
- Risk coverage - High-priority area testing thoroughness
Quality Metrics:
- Defect detection rate - Issues found during testing vs. production
- Defect escape rate - Bugs that reach production despite testing
- Customer satisfaction scores - User feedback and experience ratings
Efficiency Metrics:
- Testing productivity - Test cases executed per unit of time
- Cost per defect - Investment required to find and fix issues
- Time to market impact - Testing's effect on delivery schedules
Continuous Improvement:
- Baseline establishment - Initial measurement for comparison
- Trend tracking - Changes in metrics over time
- Root cause analysis - Understanding factors driving metric changes
- Action planning - Systematic approach to addressing improvement opportunities
Conclusion
Manual QA testing services remain essential for delivering high-quality software applications that meet user expectations and business requirements. Despite technological advances in automation and AI, the human element in testing provides irreplaceable value through creativity, intuition, and contextual understanding.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic value - Manual testing provides unique insights that automated tools cannot replicate
- Quality assurance - Human testers excel at discovering usability issues and user experience problems
- Cost effectiveness - Manual testing offers superior ROI for specific project types and scenarios
- Future evolution - The integration of AI tools will enhance rather than replace human testing capabilities
Success Factors
- Hybrid approaches - Combining manual testing expertise with emerging technologies
- Continuous learning - Staying current with testing trends and methodologies
- Quality focus - Prioritizing effectiveness over efficiency in critical testing scenarios
- Strategic implementation - Choosing appropriate testing approaches based on project characteristics
Organizations that strategically combine manual testing expertise with emerging technologies will achieve optimal quality outcomes while maintaining cost-effective testing operations. The future of manual testing lies in intelligent collaboration between human testers and AI systems, creating hybrid approaches that maximize both efficiency and effectiveness in software quality assurance.
Get a proposal today → or Speak to a QA Specialist →


